Explain How Different Enzymes Assist in the Replication of Dna.
Locating the positions of DNA-binding sites in a genome. Our annotated video script templates contain an informal version of our video script with slight improvements to define sentences and remove filler words to help with.

What Are The Steps Of Dna Replication
Which property of DNA double helix led Watson and Crick to hypothesise semi-conservative mode of DNA replication.
. Annotated Video Script TEMPLATES. Select recaps are different from the FREE recaps only because they include their own answer key and tend to focus on a more specialized topic. The DNA damage response kinases ATM activated by MRE11RAD50NBS1 MRN at the break 38 ATR activated by single-stranded DNA and replication protein A sensors 255256257258259 and DNA.
The cell from the Latin word cellula meaning small room is the basic structural and functional unit of lifeEvery cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. The first step in transcription is initiation when the RNA pol binds to the DNA upstream 5 of the gene at a specialized sequence called a promoter Figure 2a. Explain the role of enzymes in cells.
To unlock this lesson you must be a. The two parent strands can further be classified as leading strand or lagging strand and are distinguished by the continuous or discontinuous. Watson and Crick noted that the two DNA strands are anti-parallel complementary to each other with regards to their base sequences which facilitates each strand to serve as a template to synthesize a new strand.
DNA is not completely unwound during replication. DNA is the master molecule which posseses the genetic information about the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. 1 Infectious virions contain in their inner icosahedral core the genome as a partially double-stranded circular but not covalently closed DNA of about 32 kb in length relaxed circular or RC-DNA.
The two new daughter DNA molecules each contain one pre-existing strand and one newly synthesized strand. In bacteria promoters are. Learn the definition of structural isomers and explore the three types with examples of each.
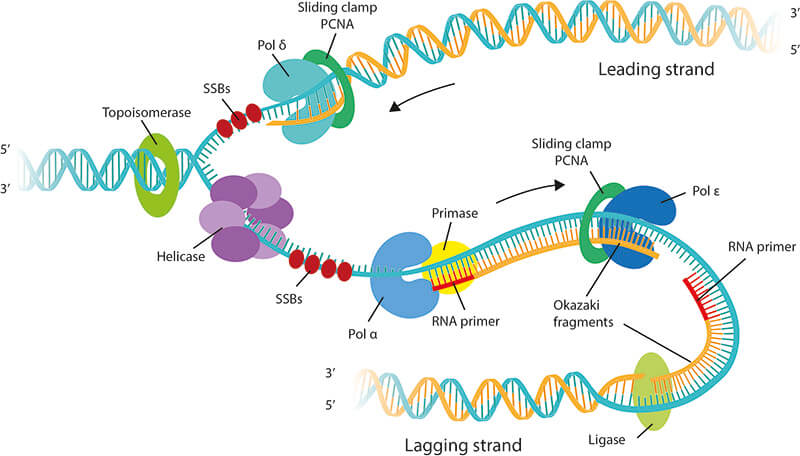
It is possible then that the modified histones may be carried into each new copy of the DNA. About and Suggested Use. Figure 317 The different enzymes associated with DNA replication.
Describe how an enzymes actions are checked or encouraged. Structure and properties of DNA regulate and control the synthesis of proteins. A biologists guide to statistical.
Recall what inputs enzymes need to assist in reactions. By altering the shape of the histones around them these modified histones would ensure that a lineage-specific. DNA present in the nucleus sends out information in the form of messenger RNA into the cytoplasm which is the site of the protein synthesis in eukaryotes.
During DNA replication a number of different enzymes work together to pull apart the two strands so each strand can be used as a template to synthesize new complementary strands. This organization of the DNA. Replication of the hepadnaviral genome can broadly be divided into three phases Figure Figure1.
This is because genetic and molecular biology experiments which we will deal with later in this chapter have shown that many of the proteins. There are a variety of online resources to assist Authors with proper statistical choices and approaches that can be found through simple internet searches for statistical tests in the biological sciences. To assist with coiling DNA is first wrapped around proteins called histones.
2 upon infection the RC-DNA is converted inside the host cell nucleus. Elongation describes the assembly of new DNA daughter strands from parent strands. Often the first thing that is discovered about a DNA-binding protein is not the identity of the protein itself but the features of the DNA sequence that the protein recognizes.
Restriction enzymes DNA methyltransferases and homing endonucleases should be named or referred to using the conventions. Once there these histones may act as templates initiating the surrounding new histones to be shaped in the new manner. Thus DNA replication is said to be semiconservative Stage 1.
Cells can acquire specified function and carry out various tasks within the cell such as replication DNA repair protein synthesis and motility. Structural isomers show the different ways atoms of molecules with the same formula are arranged.

Major Enzymes Biology For Majors I
Topic 2 7 Dna Replication Transcription And Translation Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green

Dna Replication The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Major Enzymes Biology For Majors I
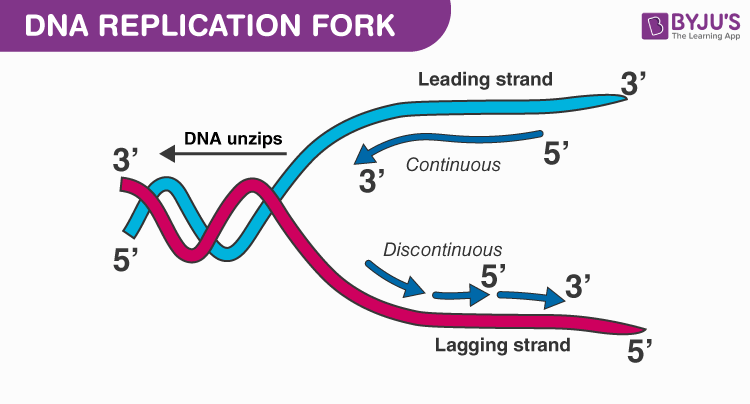
Dna Replication Process With Diagrams Class 12 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Dna Replication

Dna Replication Definition Enzymes Steps Mechanism Diagram

Dna Replication Steps Diagram Expii
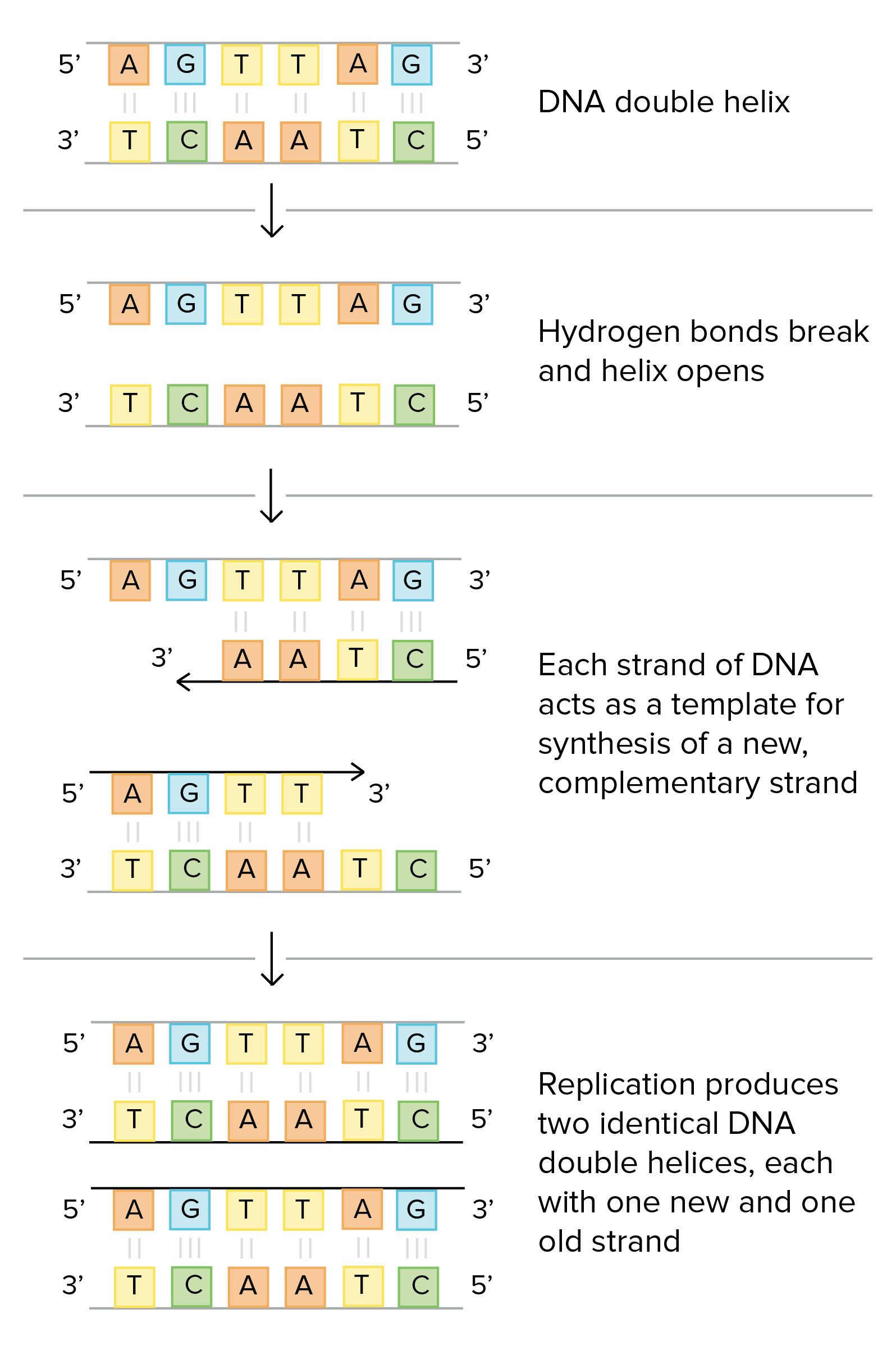
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
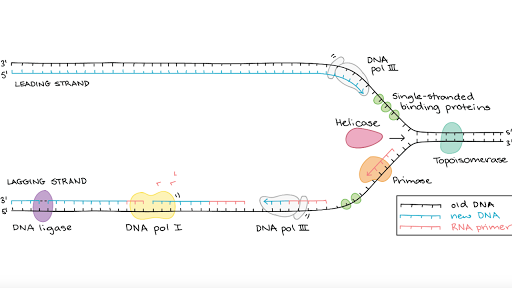
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
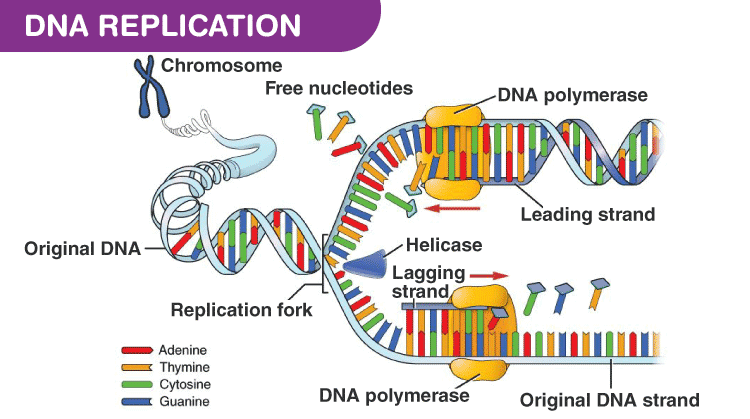
Dna Replication Process With Diagrams Class 12 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Dna Replication
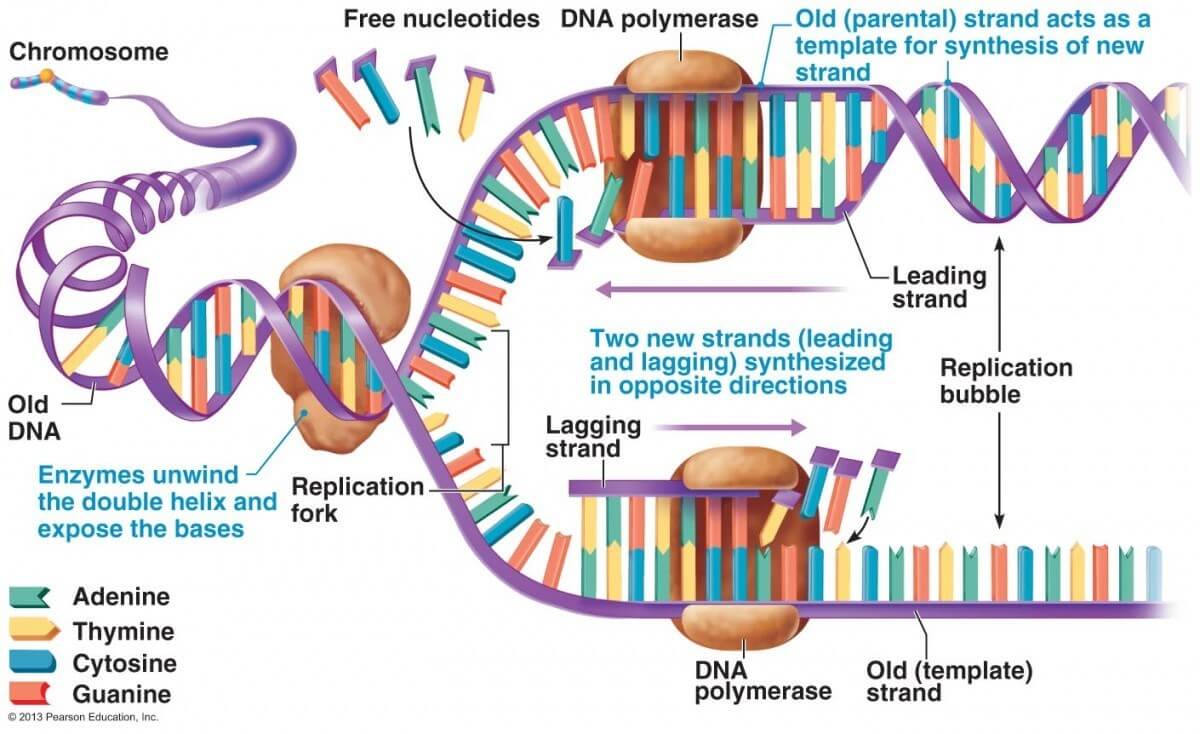
Dna Replication Study Guide Inspirit
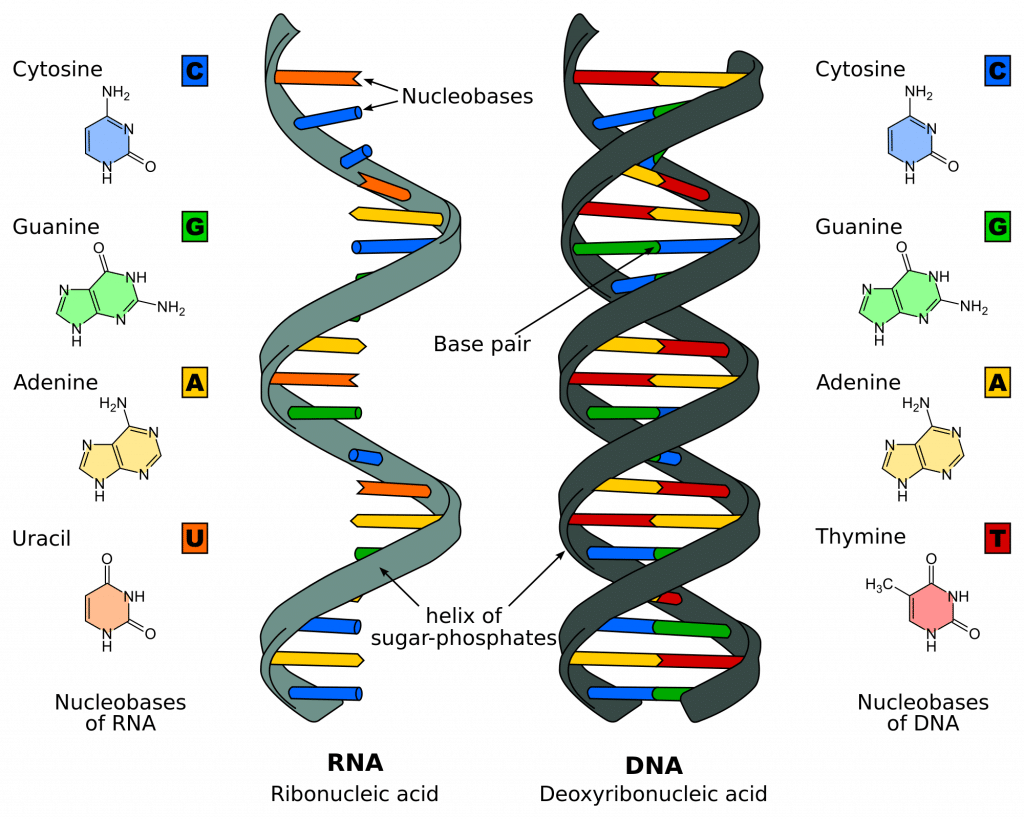
Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology

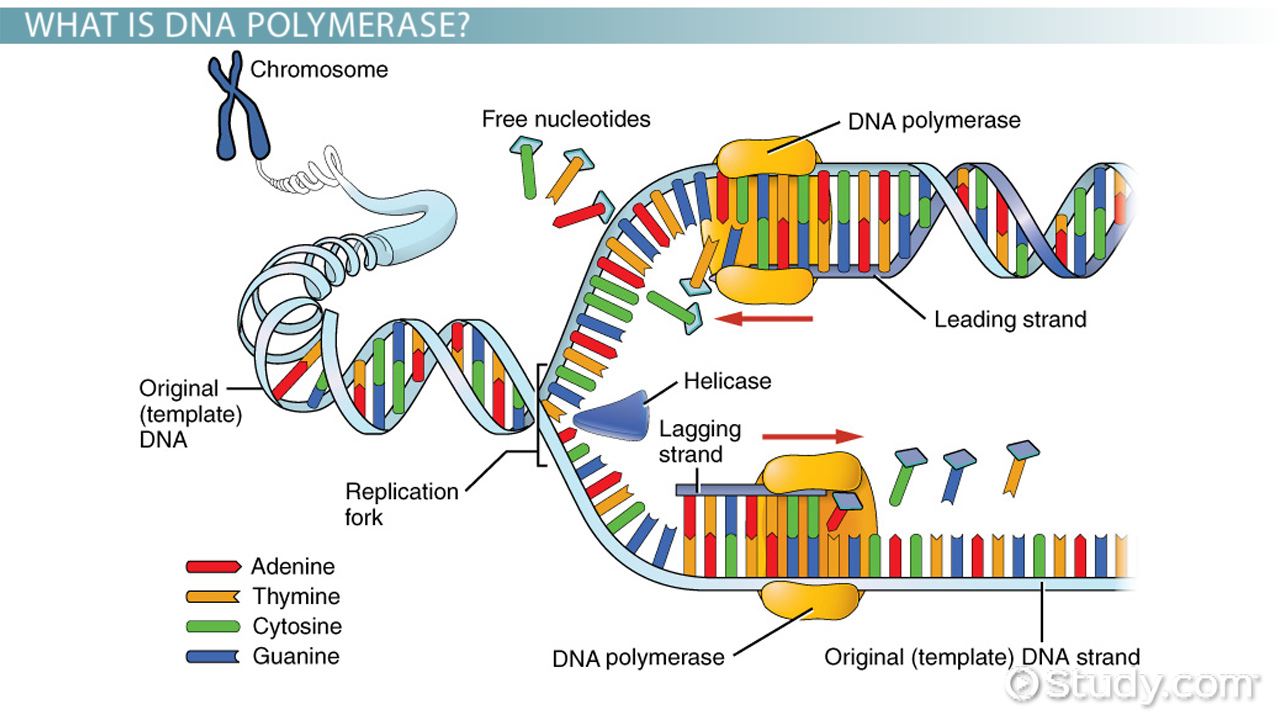
Dna Replication Enzymes Order What Enzymes Are Used In Dna Replication Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
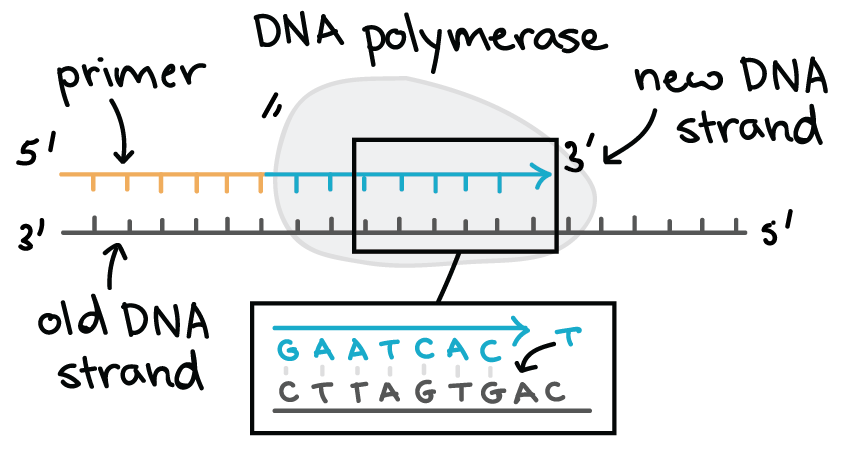
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
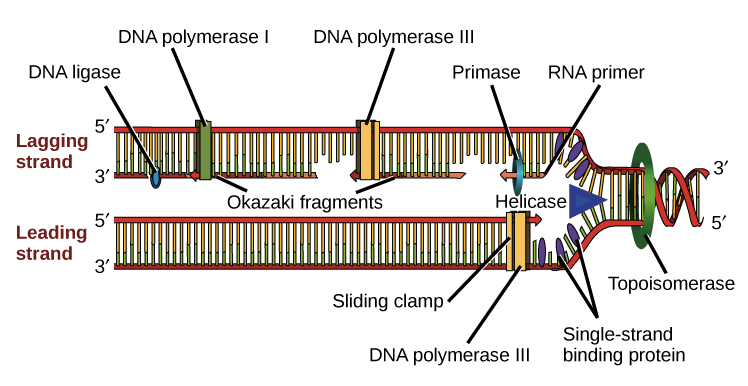
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry

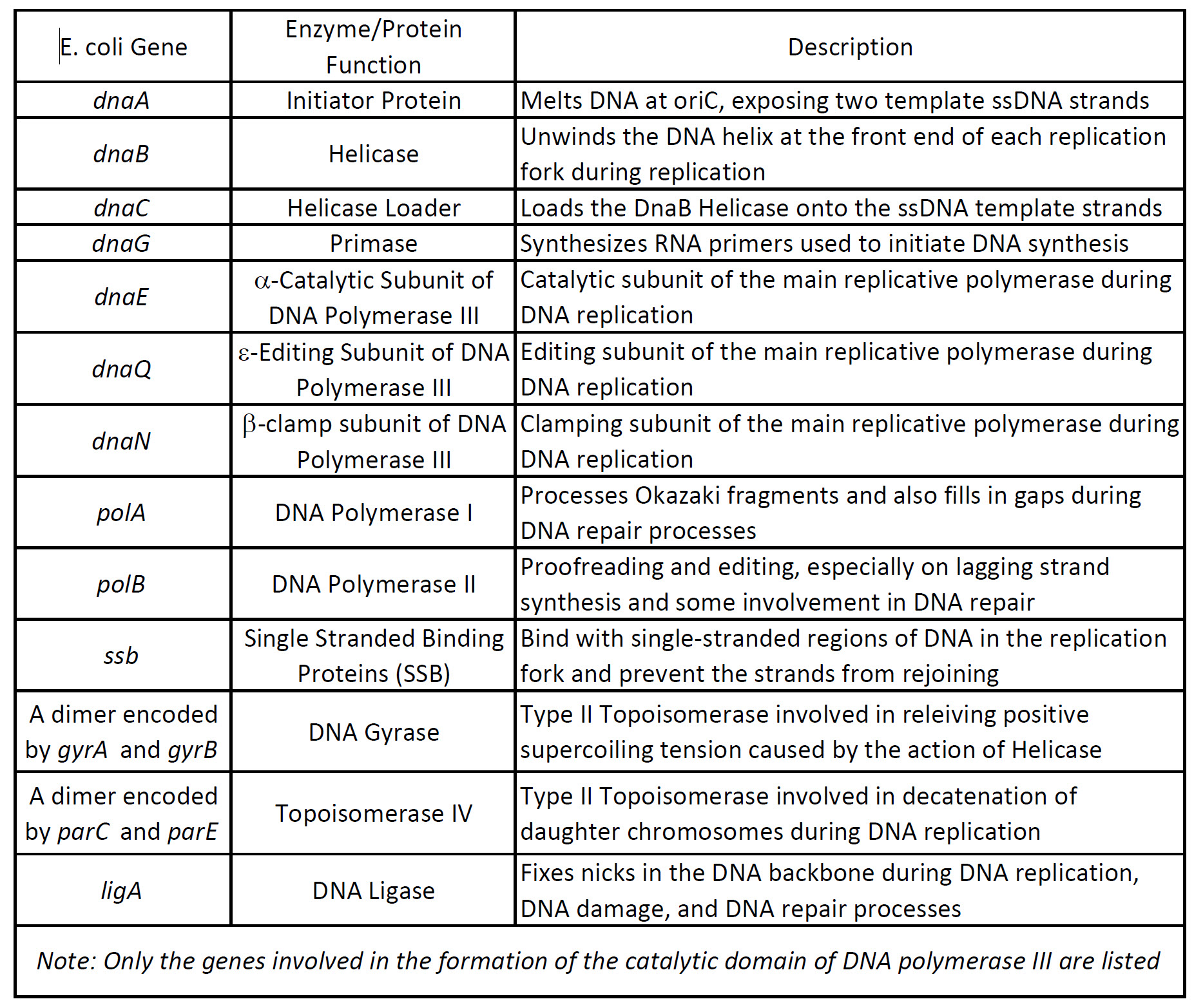
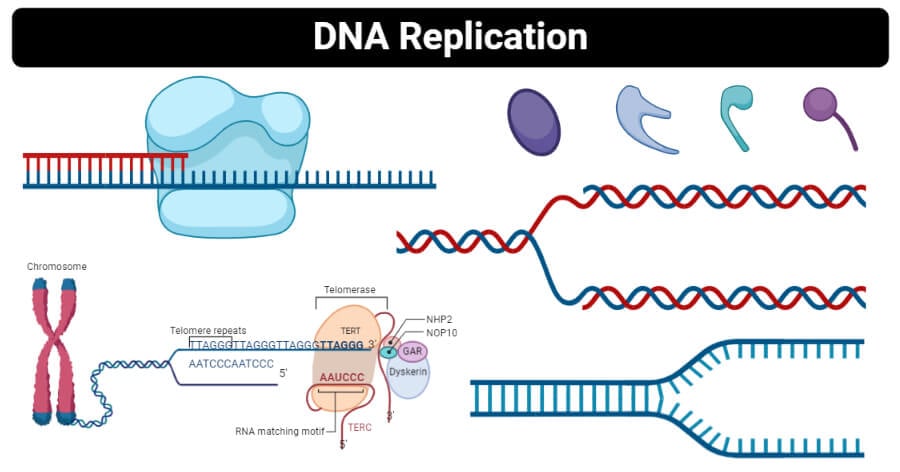
Comments
Post a Comment